Creating intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces
Creating intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces
28 Mei 2024
28 Mei 2024
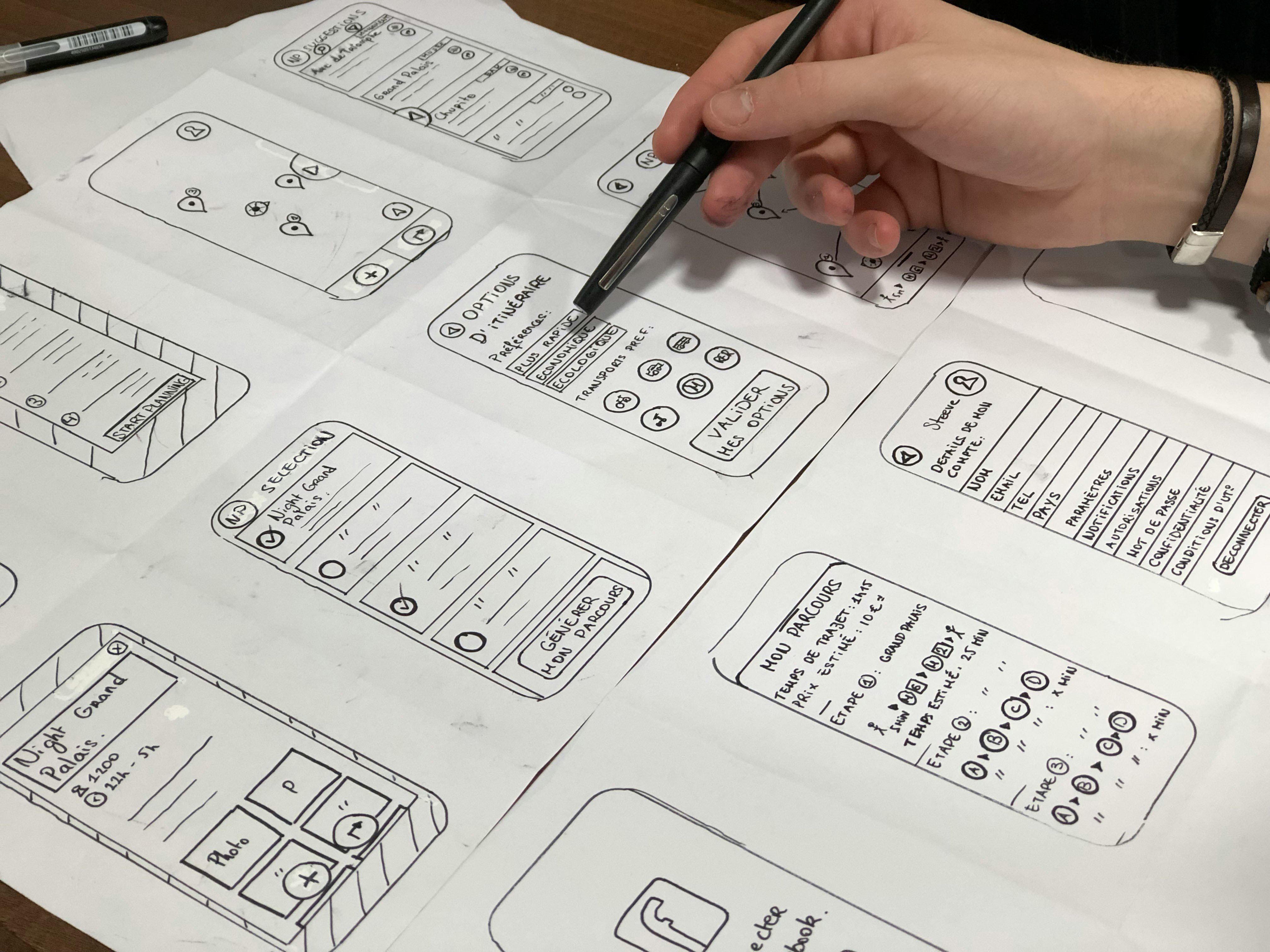

Image by Amélie Mourichon
Drag-and-drop interfaces offer users a flexible and intuitive way to interact with digital content, allowing them to manipulate objects, rearrange elements, and perform tasks with ease. Designing user-friendly drag-and-drop interactions involves simplifying complex tasks through intuitive design and providing clear visual feedback to guide users' actions. Here's how to create intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces.
Clear Visual Affordances
Use clear visual affordances to indicate draggable elements and drop targets. Design draggable objects with visual cues such as handles, shadows, or borders to signify their interactive nature. Use contrasting colors or animations to highlight drop zones and provide feedback when users hover over or interact with them.
Consistent Behavior
Maintain consistency in drag-and-drop behavior across the interface. Ensure that draggable elements behave predictably and respond to user input consistently throughout the application. Use familiar gestures and conventions to minimize cognitive load and make interactions more intuitive for users.
Progressive Disclosure
Adopt a progressive disclosure approach to guide users through complex drag-and-drop interactions. Break down tasks into smaller, manageable steps and reveal additional functionality or options as users progress through the interaction. Use tooltips, hints, or onboarding tutorials to introduce users to drag-and-drop functionality and provide guidance as needed.
Responsive Design
Design drag-and-drop interfaces with responsiveness in mind to accommodate different devices and screen sizes. Ensure that draggable elements and drop targets are accessible and easy to interact with on both desktop and mobile devices. Use responsive layouts and fluid design principles to adapt the interface to various viewport sizes and orientations.
Smart Snap and Alignment
Incorporate smart snap and alignment features to help users position draggable elements precisely. Use grid-based layouts, magnetic snapping, or alignment guides to assist users in aligning objects accurately and maintaining visual consistency. Provide visual feedback, such as snap indicators or alignment markers, to confirm successful placement.
Undo and Redo Functionality
Implement undo and redo functionality to allow users to revert or repeat drag-and-drop actions as needed. Provide users with the ability to undo accidental moves or changes and restore previous states of the interface. Use clear affordances, such as undo buttons or keyboard shortcuts, to make these features easily accessible to users.
Accessibility Considerations
Ensure that drag-and-drop interfaces are accessible to users with disabilities or impairments. Provide alternative methods for performing drag-and-drop actions, such as keyboard shortcuts or assistive technologies. Use semantic markup and ARIA roles to convey drag-and-drop functionality to screen readers and assistive devices.
Feedback and Animation
Offer immediate visual feedback to confirm drag-and-drop actions and reassure users of successful interactions. Use animations, transitions, or sound effects to indicate movement, dropping, or snapping of objects. Provide feedback messages or tooltips to inform users of the outcome of their actions and guide them through the interaction process.
User Testing and Iteration
Conduct user testing to evaluate the effectiveness and usability of drag-and-drop interfaces with real users. Observe users as they interact with the interface and gather feedback on their experiences, pain points, and preferences. Use insights from user testing to identify areas for improvement and iteratively refine the design based on user feedback.
Performance Optimization
Optimize the performance of drag-and-drop interactions to ensure smooth and responsive user experiences. Minimize latency and lag by optimizing code, reducing unnecessary animations, and prioritizing critical rendering paths. Test the interface under different load conditions and devices to identify performance bottlenecks and address them accordingly.
By incorporating these principles and best practices, designers can create intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces that simplify complex tasks and enhance user engagement and satisfaction. By providing clear visual affordances, maintaining consistent behavior, adopting progressive disclosure, designing responsively, implementing smart snap and alignment, offering undo and redo functionality, considering accessibility, providing feedback and animation, conducting user testing and iteration, and optimizing performance, designers can empower users to interact with digital content effortlessly and efficiently.
Drag-and-drop interfaces offer users a flexible and intuitive way to interact with digital content, allowing them to manipulate objects, rearrange elements, and perform tasks with ease. Designing user-friendly drag-and-drop interactions involves simplifying complex tasks through intuitive design and providing clear visual feedback to guide users' actions. Here's how to create intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces.
Clear Visual Affordances
Use clear visual affordances to indicate draggable elements and drop targets. Design draggable objects with visual cues such as handles, shadows, or borders to signify their interactive nature. Use contrasting colors or animations to highlight drop zones and provide feedback when users hover over or interact with them.
Consistent Behavior
Maintain consistency in drag-and-drop behavior across the interface. Ensure that draggable elements behave predictably and respond to user input consistently throughout the application. Use familiar gestures and conventions to minimize cognitive load and make interactions more intuitive for users.
Progressive Disclosure
Adopt a progressive disclosure approach to guide users through complex drag-and-drop interactions. Break down tasks into smaller, manageable steps and reveal additional functionality or options as users progress through the interaction. Use tooltips, hints, or onboarding tutorials to introduce users to drag-and-drop functionality and provide guidance as needed.
Responsive Design
Design drag-and-drop interfaces with responsiveness in mind to accommodate different devices and screen sizes. Ensure that draggable elements and drop targets are accessible and easy to interact with on both desktop and mobile devices. Use responsive layouts and fluid design principles to adapt the interface to various viewport sizes and orientations.
Smart Snap and Alignment
Incorporate smart snap and alignment features to help users position draggable elements precisely. Use grid-based layouts, magnetic snapping, or alignment guides to assist users in aligning objects accurately and maintaining visual consistency. Provide visual feedback, such as snap indicators or alignment markers, to confirm successful placement.
Undo and Redo Functionality
Implement undo and redo functionality to allow users to revert or repeat drag-and-drop actions as needed. Provide users with the ability to undo accidental moves or changes and restore previous states of the interface. Use clear affordances, such as undo buttons or keyboard shortcuts, to make these features easily accessible to users.
Accessibility Considerations
Ensure that drag-and-drop interfaces are accessible to users with disabilities or impairments. Provide alternative methods for performing drag-and-drop actions, such as keyboard shortcuts or assistive technologies. Use semantic markup and ARIA roles to convey drag-and-drop functionality to screen readers and assistive devices.
Feedback and Animation
Offer immediate visual feedback to confirm drag-and-drop actions and reassure users of successful interactions. Use animations, transitions, or sound effects to indicate movement, dropping, or snapping of objects. Provide feedback messages or tooltips to inform users of the outcome of their actions and guide them through the interaction process.
User Testing and Iteration
Conduct user testing to evaluate the effectiveness and usability of drag-and-drop interfaces with real users. Observe users as they interact with the interface and gather feedback on their experiences, pain points, and preferences. Use insights from user testing to identify areas for improvement and iteratively refine the design based on user feedback.
Performance Optimization
Optimize the performance of drag-and-drop interactions to ensure smooth and responsive user experiences. Minimize latency and lag by optimizing code, reducing unnecessary animations, and prioritizing critical rendering paths. Test the interface under different load conditions and devices to identify performance bottlenecks and address them accordingly.
By incorporating these principles and best practices, designers can create intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces that simplify complex tasks and enhance user engagement and satisfaction. By providing clear visual affordances, maintaining consistent behavior, adopting progressive disclosure, designing responsively, implementing smart snap and alignment, offering undo and redo functionality, considering accessibility, providing feedback and animation, conducting user testing and iteration, and optimizing performance, designers can empower users to interact with digital content effortlessly and efficiently.
Drag-and-drop interfaces offer users a flexible and intuitive way to interact with digital content, allowing them to manipulate objects, rearrange elements, and perform tasks with ease. Designing user-friendly drag-and-drop interactions involves simplifying complex tasks through intuitive design and providing clear visual feedback to guide users' actions. Here's how to create intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces.
Clear Visual Affordances
Use clear visual affordances to indicate draggable elements and drop targets. Design draggable objects with visual cues such as handles, shadows, or borders to signify their interactive nature. Use contrasting colors or animations to highlight drop zones and provide feedback when users hover over or interact with them.
Consistent Behavior
Maintain consistency in drag-and-drop behavior across the interface. Ensure that draggable elements behave predictably and respond to user input consistently throughout the application. Use familiar gestures and conventions to minimize cognitive load and make interactions more intuitive for users.
Progressive Disclosure
Adopt a progressive disclosure approach to guide users through complex drag-and-drop interactions. Break down tasks into smaller, manageable steps and reveal additional functionality or options as users progress through the interaction. Use tooltips, hints, or onboarding tutorials to introduce users to drag-and-drop functionality and provide guidance as needed.
Responsive Design
Design drag-and-drop interfaces with responsiveness in mind to accommodate different devices and screen sizes. Ensure that draggable elements and drop targets are accessible and easy to interact with on both desktop and mobile devices. Use responsive layouts and fluid design principles to adapt the interface to various viewport sizes and orientations.
Smart Snap and Alignment
Incorporate smart snap and alignment features to help users position draggable elements precisely. Use grid-based layouts, magnetic snapping, or alignment guides to assist users in aligning objects accurately and maintaining visual consistency. Provide visual feedback, such as snap indicators or alignment markers, to confirm successful placement.
Undo and Redo Functionality
Implement undo and redo functionality to allow users to revert or repeat drag-and-drop actions as needed. Provide users with the ability to undo accidental moves or changes and restore previous states of the interface. Use clear affordances, such as undo buttons or keyboard shortcuts, to make these features easily accessible to users.
Accessibility Considerations
Ensure that drag-and-drop interfaces are accessible to users with disabilities or impairments. Provide alternative methods for performing drag-and-drop actions, such as keyboard shortcuts or assistive technologies. Use semantic markup and ARIA roles to convey drag-and-drop functionality to screen readers and assistive devices.
Feedback and Animation
Offer immediate visual feedback to confirm drag-and-drop actions and reassure users of successful interactions. Use animations, transitions, or sound effects to indicate movement, dropping, or snapping of objects. Provide feedback messages or tooltips to inform users of the outcome of their actions and guide them through the interaction process.
User Testing and Iteration
Conduct user testing to evaluate the effectiveness and usability of drag-and-drop interfaces with real users. Observe users as they interact with the interface and gather feedback on their experiences, pain points, and preferences. Use insights from user testing to identify areas for improvement and iteratively refine the design based on user feedback.
Performance Optimization
Optimize the performance of drag-and-drop interactions to ensure smooth and responsive user experiences. Minimize latency and lag by optimizing code, reducing unnecessary animations, and prioritizing critical rendering paths. Test the interface under different load conditions and devices to identify performance bottlenecks and address them accordingly.
By incorporating these principles and best practices, designers can create intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces that simplify complex tasks and enhance user engagement and satisfaction. By providing clear visual affordances, maintaining consistent behavior, adopting progressive disclosure, designing responsively, implementing smart snap and alignment, offering undo and redo functionality, considering accessibility, providing feedback and animation, conducting user testing and iteration, and optimizing performance, designers can empower users to interact with digital content effortlessly and efficiently.
Siap untuk memimpin masa depan?
©2024, rajeshsiburian
Siap untuk memimpin masa depan?
©2024, rajeshsiburian
Siap untuk memimpin masa depan?
©2024, rajeshsiburian